The complete guide to the ICH Q7 guidelines
What is ICH Q7, and how can it benefit your company?
Safeguarding the quality of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) is critical for assuring the overall quality of the drugs they flow into — and it's here that ICH Q7 guidelines offer a valuable model for pharmaceutical quality and compliance professionals.
Simply put: if you manufacture APIs, you should take a good look at ICH Q7's requirements.
In this article, we’ll explore what ICH Q7 is, review its key components, and explain how to effectively embed ICH Q7 guidelines into your company.
What is ICH Q7?
ICH Q7 is a guideline issued in 2000 by the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. (We'll just call them ICH, for obvious reasons!)
It maps out a subset of Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) specifically for active pharmaceutical ingredients: the biologically active substances within drugs that give them their efficacy.
ICH's 1998 concept paper reveals why. Back then, ICH identified a gap in how 'starting materials' (pharmaceutical ingredients) were assessed in accordance with Good Manufacturing Practice.
It noted that, "in many countries there is no compulsory inspection scheme nor even the possibility to establish GMP certificates for starting materials".
ICH Q7 guidelines therefore set a global quality management standard for the production and control of the APIs that make up pharmaceutical drugs. It ensures that APIs meet the quality and purity characteristics they are purported to possess.
The main objectives of ICH Q7 are to:
-
Close the gap in pharmaceutical ingredient quality assurance by offering a global GMP standard for API manufacturers
-
Prevent risks associated with contaminated, impure or adulterated APIs
-
Create a harmonized framework for API manufacturers to be inspected and assessed by bodies like the FDA or EMA
Like other ICH quality guidelines — Q8, Q9 and Q10, for example — ICH Q7 isn't mandatory. But it's widely recognized as the 'gold standard' for compliant API manufacture, and its requirements bleed into the expectations of regulatory bodies around the world, such as the EU's EudraLex GMP Part II.
And ICH Q7 isn't necessarily just for API companies themselves. Any contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) who do outsourced production work for them, as well as API testing labs and pharmaceutical companies sourcing APIs internationally, should all familiarize themselves with, and work towards, the ICH Q7 guidelines.
ICH Q7 guidelines
ICH Q7 covers a wide range of API quality management topics, structured into 20 sections (including intro and glossary).
These sections are designed by ICH to offer comprehensive guidance on every aspect of API production, from raw material sourcing to shipment of final product.
Of course, there's no alternative to reading the full ICH Q7 guidelines, which are too comprehensive to explain in detail here.
But here's a summary of some of the key requirements you should start thinking of and building into your organization.
1. Quality management
First and foremost, your company should establish a comprehensive, overarching quality management system that structures all other work. This includes an independent quality unit, responsible for reviewing and approving all procedures and quality-related documents.
It makes sense to look to ICH's pharmaceutical quality system guidelines, ICH Q10, for inspiration and cross-pollination here.

2. Personnel
Employees should have the appropriate qualifications, training and experience to discharge their roles competently. Roles and responsibilities must be clearly defined. Adequate hygiene programs are also mandated.
3. Buildings and facilities
Just like in other GMP guidelines, such as FDA 21 CFR Part 211, your facilities should be designed, maintained and frequently cleaned to prevent contamination and mix-ups. Critical utilities (water systems, HVAC, and so on) must be validated, and a mixture of 'technical' and 'procedural' controls should be in place to keep buildings, facilities and containment areas clean and optimized.
4. Process equipment
Equipment must be of appropriate design, and regularly cleaned and maintained. Documentation is required for equipment use, cleaning and maintenance.
5. Documentation and records
Like pretty much every set of quality management guidelines ever written, ICH Q7 stresses the importance of accurate, complete and accessible documentation. This includes batch records, SOPs, test results and deviations — all underpinned by typical regulated document activities like version control, managed access and legally binding signatures from responsible personnel.
Good Documentation Practice (GDocP) is a useful framework to consider here, and to tie in with your ICH Q7 GMP activities. Pharmaceutical GxP is, after all, designed to be an overarching and connective umbrella.
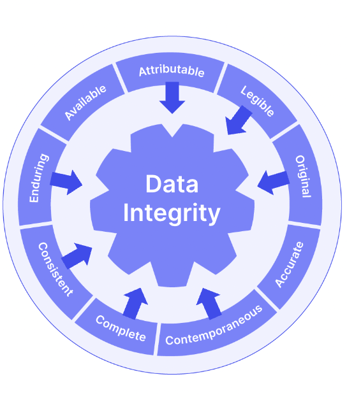
ALCOA+, too, is a useful supportive guideline.
6. Materials management
Raw materials should be stored and handled to prevent degradation or contamination. Each material should have a unique identifier and status label, so you can instantly separate approved materials from quarantined, for instance.
7. Production and in-process controls
The heart of your API production activity. Manufacturing operations must be thoroughly documented, and in-process, 'scientifically sound' sampling and controls must be carried out and recorded to assure quality during the manufacturing process. Deviations must be thoroughly checked with an out-of-specification (OOS) investigation.
8. Packaging and labeling
Proper GMP labeling prevents product mix-ups and contamination. Packaging materials must meet the specified quality requirements.
9. Laboratory controls
Analytical labs must use validated methods and maintain them thorough documentation. All testing must meet predefined specifications.
10. Validation
Processes and systems that impact product quality must be validated, including cleaning procedures, analytical methods and computer systems — including critical tools like pharmaceutical quality management software.
Read our guide to the pharmaceutical software systems your company needs
ICH Q7 Good Manufacturing Practice
As you'd expect, GMP under ICH Q7 is all about maintaining optimal API quality through well-defined and consistently executed processes.
There are a few critical operational elements to consider to kick off your ICH Q7 journey.
1. Process consistency
Implement standard operating procedures (SOPs) for all stages of API production. Ensure strict adherence through training, auditing and good documentation practice.
2. Risk management
Identify risks in the manufacturing process and implement mitigation strategies. For instance, prevent cross-contamination by segregating equipment for different products.
Use ICH Q9 for inspiration!
3. Change control
ICH Q7 mandates a robust change control system.
Any changes to processes, equipment or materials must be:
-
Reviewed by your quality unit
- Documented and approved before implementation
-
Evaluated for impact on product quality. Consider applying ICH Q8 quality by design (QbD) principles to identify and control your API's critical material attributes (CMAs), and how they flow into the finished drug's quality target product profile (QTPP)

4. Internal audits
Routine internal audits of your ICP manufacturing set-up, and your broader pharmaceutical quality system, help identify gaps before your regulators do.
Develop an audit schedule, and keep clear records of findings and corrective and preventive actions.
5. Environmental monitoring
Especially in sterile or critical areas, environmental monitoring ensures a clean and controlled environment. Regular air, surface and personnel monitoring are part of the ICH Q7 guidelines' expectations.
6. Supplier qualification
Only qualified suppliers should be used for raw materials. Establish a supplier qualification program including a risk-based audit schedule, quality agreements (QAgs), and regular performance evaluations.
ICH Q7 questions and answers
Got some burning questions about the ICH Q7 guidelines?
We assembled a quick Q&A to give you more info.
Can I use non-dedicated equipment for multiple products?
Yes, but you must have robust cleaning validation and demonstrate that cross-contamination is avoided.
Do APIs require expiry dates?
Yes. APIs must have a defined retest or expiry date based on stability data.
How should reprocessing be handled?
Reprocessing is allowed, but it must be predefined, documented and validated. Reworking is more restricted and requires approval by the quality unit.
Are electronic signatures acceptable?
Yes, if they meet 21 CFR Part 11 requirements (or equivalent), including secure access, audit trails and system validation.
What happens if we use contract manufacturing?
A: The responsibility for quality remains with you, the sponsor company. Any CMO agreement must define roles and responsibilities, and your contractor must follow ICH Q7 on your behalf.
What is the role of the quality unit under ICH Q7?
The quality unit must be independent, and has final authority over key activities like batch release, deviation handling and change control. They don't necessarily need to perform activities like testing and sampling — ICH Q7 is flexible on that point — but the process roles and responsibilities agreed within the company need to be thoroughly documented and overseen by the quality unit.
How should out-of-specification (OOS) results be handled?
All OOS results must be thoroughly investigated. Root cause analysis, retesting and batch disposition decisions must be fully documented and ready for inspection by an auditor.
How often should product quality reviews take place?
An annual review is typical and expected, but you can tweak your timeframes to higher or lower frequency with proper justification.
Can digital quality tools simplify ICH Q7 compliance?
Yes.
Best-in-class pharmaceutical quality management software systems, like Qualio, make adherence to ICH Q7 GMP guidelines a natural and automatic part of your business.
The best pharma quality software systems work by centralizing information, by letting you build flexible and fully trackable digital workflows for sharing actions, and by offering a single, integrated quality system for activities like document review, training, OOS investigations, and more.
Embracing the ICH Q7 guidelines in your business
As we've seen, meeting ICH Q7 guidelines is now more or less expected for any pharmaceutical company involved in the production or handling of active pharmaceutical ingredients.
Successfully implementing ICH Q7 requires careful combination of:
-
A strong quality management system
-
Thorough, properly maintained documentation
-
Robust training programs
-
Effective validation processes
-
Strict facility and material controls
Organizations that adopt the ICH Q7 principles position themselves for optimal, fully compliant API manufacture.
