The complete guide to passing ISO 13485 audits
ISO 13485 audits are a vital quality and compliance hurdle for medical device companies to tackle.
Understanding the ISO 13485 audit process, both for 'real deal' third-party audits and your own internal audit preparations, is essential for international medical device market success.
We've built this audit guide to get you confident, compliant and ready for that knock on the door.
Table of Contents
What is an ISO 13485 audit?
ISO 13485 audits are, in short, an examination of your company to see if it conforms to modern expectations of medical device quality management.
A quality management system (QMS) is the way your organization directs and controls those activities that are related, either directly or indirectly, to achieving your intended operational results.
It consists of your organization’s structure together with the planning, processes, resources, documents and records that you use to hit your quality objectives.
ISO 13485 is the industry standard for medical device quality management.
If you want an internationally recognized stamp of approval for your medical device QMS, you can work towards conformance with ISO 13485 as a documented set of interrelated processes, including any forms or templates, that establish, implement, and maintain the requirements of the standard.
This is with the aim of meeting customer and regulatory requirements for businesses operating in the medical device sector. These processes and their interactions are also subject to improvement as directed by senior management to achieve quality objectives.
An audit is:
'... a systematic, independent and documented process for obtaining objective evidence and evaluating it objectively to determine the extent to which the audit criteria are fulfilled...'
ISO 13485 audits, then, are an examination of your company's quality management system processes to assess the extent to which you're meeting the requirements of the ISO 13485:2016 standard.
ISO 13485 audit requirements
The objective of ISO 13485 audits is to determine if all applicable requirements of ISO 13485:2016 have been implemented in your company.
The audit objectives specifically include evaluation of:
- The effectiveness of your QMS in incorporating the applicable regulatory requirements
- Product/process-related technologies
- Adequate product technical documentation in relation to relevant regulatory requirements
- Your ability to comply with these requirements
As part of achieving these ISO 13485 audit objectives, the auditor will verify that your organization maintains sufficient and reliable objective evidence to demonstrate your devices meet essential principles of safety, performance and effectiveness.
The auditor will expect that your documentation and records are maintained to demonstrate continued compliance with regulatory requirements during the post-market phase of the device lifecycle.
And you'll need to prove an effective risk-based approach is in place.
Implementing a risk-based approach is an integral aspect of a medical device organization’s quality management system, and it's the responsibility of top management to provide the necessary commitment and resources for this effort.
Effective implementation of the risk-based approach usually starts in conjunction with the design and development process, proceeds through product realization (including the selection of suppliers), considers feedback from post-market monitoring, and continues until the time your device is decommissioned.
Risk-based decisions occur throughout the various quality management system processes, and each medical device organization must implement the risk-based approach as well as risk management in product realization with a determination of how much residual risk is acceptable to ensure their medical devices meet requirements for safety, performance and regulatory requirements.
How to prepare for an ISO 13485 audit
In an external third-party ISO 13485 audit, your medical device organization needs to demonstrate its ability to provide medical devices that consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
The failure to fulfil any of the requirements in ISO 13485:2016, or portion of the requirements listed in the audit activities and tasks, means audit failure, delay or reversal of your ISO 13485 accreditation, and a significant backward step in your medical device company's operational plans.
ISO 13485 audit questions and answers
Like any test or examination, knowing the questions you'll be asked, and how you'll answer them, is the key to success for ISO 13485 audits.
The next section of this post will provide a detailed ISO 13485 checklist outlining every clause-by-clause question that will be asked of your medical device QMS.
But particular attention should also be paid to the potential interrelationship of processes in your company that may lead to significant nonconformity in an ISO 13485 audit.
The output of one process often directly forms the input of other processes, and the activities of a supporting process can be relevant to other processes.
For example, during an ISO 13485 audit the auditor could find non-conformances in both your purchasing controls and your acceptance activities.
Individually, 'failing' one of these questions on your audit may amount to a minor nonconformity.
But together they indicate a significant nonconformity, because control over suppliers and the products they supply depends on an effective mix of both these activities, and deficiencies in both will affect the quality of your finished device.
A zero-sum 'question-and-answer' approach can only get you so far in your ISO 13485 audit preparations.
The interaction between areas of your medical device QMS is as significant as the individual strength of each ingredient.
ISO 13485 audit checklist
With that caveat out of the way, we recognize that often the best way to prepare for an ISO 13485 audit is a reassuring, tick-by-tick 'shopping list' approach as you assess your medical device QMS for weaknesses.
As such, the Qualio+ team has assembled a comprehensive ISO 13485 audit checklist to help you prepare.
How to conduct an ISO 13485 audit
How should your business conduct an ISO 13485 audit, then?
That depends on the type of audit we're discussing.
It's worth familiarizing yourself with the different types of audits before we start digging deeper:

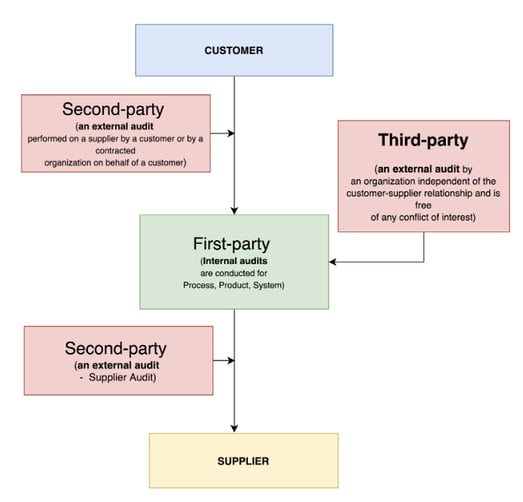
Internal audits
An internal or first-party ISO 13485 audit is your 'dry run' practice audit, and the best way to prepare for a real third-party regulatory audit.
We'll dig into how to conduct an ISO 13485 internal audit in detail a little further down.
But it's worth noting here that you should always ensure your internal auditing meets the expectations or 'principles' of modern auditing as laid out in ISO 19011:
- Integrity
- Fair presentation
- Due professional care
- Confidentiality
- Independence
- Evidence-based approach
A useful component of internal auditing is its ability to enforce standardization. By pinpointing areas of variation and difference that threaten your ISO 13485 compliance, you can take corrective action to fix those issues and make your company work in a more standardized way.
Watch our guidance video!
Audits & inspections: how to drive a standardization strategy that sticks
Supplier audits
A supplier audit can cut both ways: either your customer audits you as a supplier to check your ISO 13485 compliance, or you audit one of your own suppliers.
Remember that your ISO 13485 compliance can hinge upon what your suppliers do: failing to onboard suppliers properly, and introducing defective parts and materials into your own company will stop you getting accredited to ISO 13485, even if it's your supplier's 'fault'.
Download the essential guide to life science supplier management
External audits
The big one. An external, third-party regulatory ISO 13485 audit is your company's formal assessment to secure or maintain your ISO 13485 compliance.
External audits can be stressful events that take months to prepare for.
Some key things to consider to prepare for an ISO 13485 external audit include:
- Prepare documents in compliance with all ISO 13485 requirements
- Implement the documents as fully traceable, recorded processes
- Identify and conduct training
- Conduct a gap assessment of all SOPs and processes
- Develop and implement a comprehensive risk assessment program
- Ensure employees are trained on their ISO 13485 requirements
- Ensure employees are competent and able to fulfil their ISO 13485 requirements
- Ensure each employee knows:
- Where to find the quality policy
- What the quality policy says
- Who the management representative is
- Their job description/responsibilities
- How they contribute to maintaining the quality of the devices delivered to the customer
- Where the SOPs/QMS documents are located
- Which SOPs are applicable to their job
- Where their training records are
- How to handle nonconforming products/results
- Quality objectives
Conducting an ISO 13485 internal audit
Of the three types discussed above, first-party internal audits are the most important to master. Nail those, and passing a second- or third-party ISO 13485 audit becomes much, much easier.
There are three main areas to consider: structuring your internal audit with a clear schedule of activity, following a checklist to ensure nothing's missed, and ensuring your audit team is properly trained and competent.
ISO 13485 internal audit schedule
An ISO 13485 internal audit schedule should include space for all key audit activities, including:
- Audit prep
- Conducting document review
- Conducting onsite audit activities
- Preparation, approval and distribution of audit report
- Completing the audit
- Follow-up audit(s)
- Addressing findings
Your schedule should include a robust ISO 13485 audit plan, covering:
- Audit objectives
- Audit criteria and reference documents
- Scope, including identification of organizational units
- Date and time of audit activities
- Audit team responsibilities
- Allocation of resources
- Auditee representatives
- Assigning work to audit team members
- Preparation of working documents
- Provision of checklists & forms for recording
ISO 13485 internal audit checklist
The detailed checklist provided above could serve as a suitable ISO 13485 internal audit checklist.
However, you may not want to dig into so much detail in every single internal audit - and a careful balance should be struck between audit neglect and overkill that exhausts your team members.
Although clause-by-clause tickbox activity can be helpful, you should also be cognisant of the topline 'buckets' of activity to check up on in individual internal audits.
They look like this.
| ISO 13485 requirement | Key ingredients |
| General requirements |
|
| Documentation |
|
| Management responsibility |
|
| HR |
|
| Infrastructure |
|
| Work environment & contamination control |
|
| Planning of product realization |
|
| Customer-related processes |
|
| Design & development |
|
| Purchasing |
|
| Production & service provision |
|
| Monitoring & measurement |
|
| Control of nonconforming product |
|
| Analysis of data |
|
| Improvement |
|
ISO 13485 internal audit training
Training yourself and your team for an internal ISO 13485 audit means mastering the key operational steps you'll need to take before, during and after the session.
These include ensuring:
- Your audit team knows how to check if your QMS conforms with all ISO 13485 requirements
- Those performing the audits have no direct responsibility for what is being audited
- Dates and results of audits are documented
- Audits are performed at defendable intervals
- Findings that require action are handled appropriately (i.e. CAPAs)
ISO 13485 audit report sample
The audit report is the most important (and visible) tool of the ISO 13485 audit.
Communicating audit results effectively requires both knowledge of the subject and the audience.
Remember the reader of your audit report could be:
- Auditee (team lead/function/department head)
- Newly assigned
- Various personnel from the function/department
- Executive management
- ISO auditor
- Quality management
- Quality personnel
- The next generation of auditors!
Take the reader who may not be familiar with the subject along a journey.
Begin with function and department responsibilities, procedures and how they fit into the overall company process(es), then describe the best practices and follow though with any identified audit findings or opportunities for improvement.
End the journey with clear, actionable persuasion and encouragement to act on the opportunities for improvement, or react to the observations (issues) that threaten your ISO 13485 compliance.
Here's a sample of an ISO 13485 audit report to help you prepare this key ingredient of your ISO 13485 audits.
| Audit report |
|
Audit Date: Scope of Audit: Audited by: Auditee Contact: Auditee Team: |
|
Opening meeting was conducted on —----- Attendees: Closing meeting was conducted on —--- Attendees: |
|
Introduction: (mention the company and device details here!)
|
|
Audit findings: Major: Minor: |
|
Opportunities for improvement:
|
Pass your ISO 13485 audits easily
Needless to say after this comprehensive tour, passing ISO 13485 audits is tough and complex.
Our recent life science quality trends report found that 49% of life science companies continue to rely on paper to manage their critical quality processes.
Paper and spreadsheets clutter and complicate your medical device quality management, making it more difficult to spot compliance weaknesses and embed repeatable processes.
More and more medical device companies like TriMed are turning to ISO 13485 compliance software to simplify and accelerate their journeys.
Book a demo with Qualio to see how digital ISO 13485 audit success works!
